Microsoft Azure is one of the leading cloud platforms, offering a wide variety of services that range from hosting simple web apps to running enterprise-grade AI solutions. Understanding the most common services in Azure can give you a strong foundation for building cloud-native applications, managing infrastructure, and scaling your projects effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore Azure’s most used services with clear explanations and practical examples for developers.
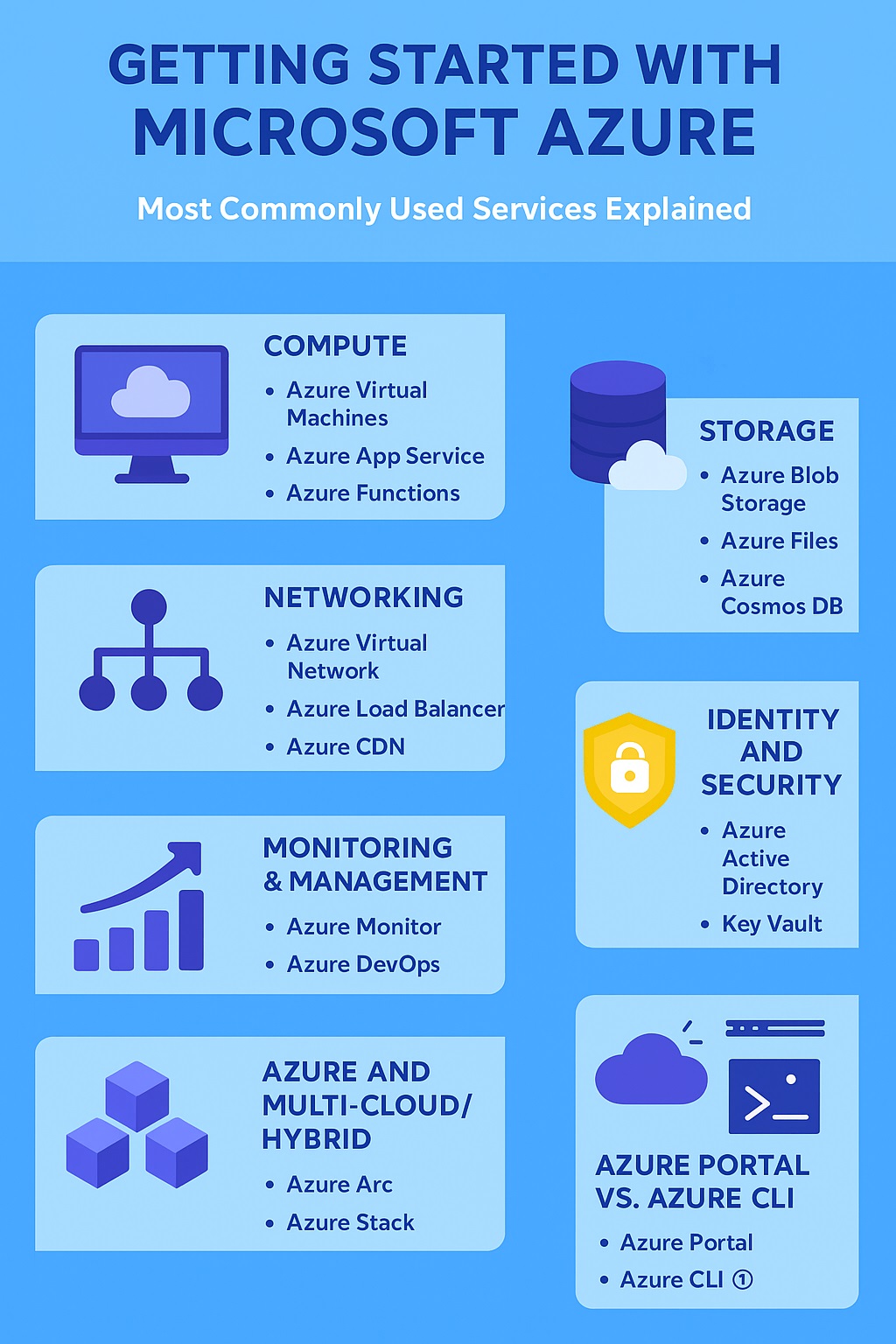
1. Azure Portal vs. Azure CLI
Before diving into services, let’s first understand how to interact with Azure:
- Azure Portal: A web-based GUI to create, configure, and manage resources. Great for beginners.
- Azure CLI: Command-line tool for developers and DevOps engineers to script and automate tasks.
Example: Creating a Resource Group with Azure CLI
# Login first
az login
# Create a resource group
az group create --name MyResourceGroup --location eastus
2. Compute Services
a) Azure Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Similar to traditional servers, but hosted in the cloud.
- Used for legacy applications, testing environments, or workloads that require full control over the OS.
Example: Create a VM using CLI
az vm create \
--resource-group MyResourceGroup \
--name MyVM \
--image UbuntuLTS \
--admin-username azureuser \
--generate-ssh-keys
b) Azure App Service
- PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service) for hosting web apps, REST APIs, and mobile backends.
- Supports .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, PHP.
Example: Deploy a Node.js app
az webapp up --name my-nodeapp --resource-group MyResourceGroup --runtime "NODE:18LTS"
c) Azure Functions
- Serverless compute model.
- Best for event-driven apps (like responding to a queue, blob upload, or HTTP request).
Example: JavaScript Azure Function
module.exports = async function (context, req) {
context.res = {
status: 200,
body: "Hello from Azure Function!"
};
};
3. Storage Services
a) Azure Blob Storage
- Stores unstructured data (images, videos, backups).
- Commonly used for static website hosting.
Upload a file to Blob Storage
az storage blob upload \
--account-name mystorageaccount \
--container-name mycontainer \
--name sample.txt \
--file ./sample.txt
b) Azure Files
- Shared network file system, accessible via SMB protocol.
- Useful for lift-and-shift scenarios where applications expect file shares.
c) Azure Cosmos DB
- Globally distributed NoSQL database.
- Supports multiple APIs (SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Gremlin, Table).
Example: Simple query with SQL API
SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.department = "Engineering"
4. Networking Services
a) Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
- Foundation for private networking in Azure.
- Connects VMs, App Services, and on-prem resources.
b) Azure Load Balancer
- Distributes incoming traffic across multiple VMs.
- Ensures high availability.
c) Azure CDN
- Delivers content globally with low latency.
- Ideal for hosting media files, static sites, and APIs.
5. Identity and Security
a) Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Centralized identity provider.
- Supports Single Sign-On (SSO) and MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication).
- Integrates with Microsoft 365 and thousands of SaaS apps.
Example: Assign a role to a user
az role assignment create \
--assignee <a href="mailto:user@domain.com" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">user@domain.com</a> \
--role Contributor \
--scope /subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/MyResourceGroup
b) Key Vault
- Securely stores secrets, API keys, certificates.
Example: Store a secret
az keyvault secret set --vault-name MyVault --name "DBPassword" --value "SuperSecret123"
6. Monitoring & Management
a) Azure Monitor
- Collects telemetry, metrics, and logs from resources.
- Integrates with Log Analytics for advanced querying.
Example: Query logs in Kusto Query Language (KQL)
AzureActivity
| where OperationName == "Create or Update Virtual Machine"
| project ResourceGroup, ActivityStatus, Caller
b) Azure DevOps
- Full DevOps platform for CI/CD pipelines, repo hosting, artifact storage.
- Alternatives: GitHub Actions (also owned by Microsoft).
7. Azure and the Cloud-Native Ecosystem
a) Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Managed Kubernetes for containerized workloads.
- Integrates with Helm, Prometheus, Grafana.
Example: Create AKS Cluster
az aks create \
--resource-group MyResourceGroup \
--name MyAKSCluster \
--node-count 2 \
--enable-addons monitoring \
--generate-ssh-keys
b) Azure Logic Apps
- Low-code solution for workflow automation.
- Connects to 200+ services (Salesforce, SAP, Outlook, etc.).
8. Azure and Multi-Cloud/Hybrid
Microsoft promotes a hybrid cloud approach:
- Azure Arc: Manage multi-cloud and on-prem workloads with a single control plane.
- Azure Stack: Run Azure services on-premise for compliance or latency-sensitive workloads.
Conclusion
Microsoft Azure is a massive ecosystem, but the most commonly used services fall into a few core categories:
- Compute: VMs, App Services, Functions
- Storage: Blob, Files, Cosmos DB
- Networking: VNet, Load Balancer, CDN
- Identity & Security: Azure AD, Key Vault
- Monitoring & DevOps: Azure Monitor, DevOps, AKS